If You Suffer From Knee and Hip Pain, You Should Read This
- Advertisement -
Knee and hip pain are among the most common complaints that affect people of all ages. These joints play a vital role in mobility, and discomfort in them can significantly impact your quality of life. Whether caused by injury, arthritis, or overuse, knee and hip pain can make even simple activities, such as walking or climbing stairs, challenging.
In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, remedies, and prevention tips for knee and hip pain. By understanding these aspects, you can take steps toward effective relief and improved joint health.
- Advertisement -
Understanding Knee and Hip Pain
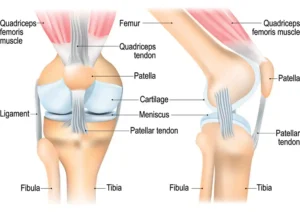
The knee and hip are complex joints that bear much of your body weight, making them susceptible to wear and tear. While knee pain often results from ligament injuries or arthritis, hip pain may stem from problems with the joint, muscles, or surrounding tissues.
| Area Affected | Common Causes |
|---|---|
| Knee | Arthritis, ligament injuries, overuse, and obesity. |
| Hip | Osteoarthritis, bursitis, hip labral tears, and trauma |
- Advertisement -
Understanding the root cause of your pain is critical to finding the right treatment.
Common Causes of Knee and Hip Pain
1. Osteoarthritis
- Advertisement -
Osteoarthritis (OA) is one of the leading causes of knee and hip pain. It occurs when the cartilage in the joints wears down over time, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Symptoms: Joint pain, decreased range of motion, and swelling.
- Who is at risk? Older adults, individuals with a family history of OA, and those who are overweight.
2. Injuries
Injuries such as ligament tears (e.g., ACL in the knee) or hip dislocations can cause acute pain. These injuries may result from sports, accidents, or sudden movements.
- Knee Injuries: Meniscus tears, ligament sprains, or fractures.
- Hip injuries can include labral tears, fractures, or muscle strains.
- Advertisement -
3. Inflammation and Overuse
Conditions like bursitis (inflammation of fluid-filled sacs in joints) or tendinitis (inflammation of tendons) can result in pain in both the knee and hip. Overuse from repetitive activities like running or cycling can exacerbate these conditions.
4. Obesity and Poor Posture
Excess body weight puts additional strain on the knee and hip joints, accelerating cartilage wear. Similarly, poor posture or gait can lead to misalignment, resulting in joint stress and pain.
Symptoms of Knee and Hip Pain
Knowing the symptoms of joint pain can help you determine its severity and when to seek medical attention:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Swelling and stiffness. | Common in arthritis and injuries. |
| Sharp or Dull Pain | Sharp pain may indicate injury; dull pain is often due to OA. |
| Limited Mobility | There is difficulty in walking, bending, or rotating the joint. |
| Clicking or popping sounds | This could suggest damage to the cartilage or a problem with the ligament. |
| Weakness | There is a sensation of unsteadiness in the joint. |
Remedies for Knee and Hip Pain
While severe cases may require medical intervention, there are several remedies you can try at home to alleviate knee and hip pain.
1. Rest and Ice Therapy
Rest and ice therapy can offer immediate relief for acute pain resulting from injury or inflammation.
- How to Use: Apply an ice pack to the affected area for 15-20 minutes, 3-4 times a day.
- Why It Works: Ice reduces swelling and numbs the area, alleviating pain.
2. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a highly effective treatment for chronic joint pain. A therapist can guide you through exercises to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pressure on the joints.
- Focus Areas:
- For the knee: Strengthen the quadriceps and hamstrings.
- For the hip: Focus on gluteal muscles and hip flexors.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Caution: Use medications as prescribed and consult a doctor if pain persists.
4. Heat Therapy
Applying heat can relax stiff muscles and improve blood circulation to the affected joints.
- Use a warm towel, a heating pad, or take a warm bath for 15–20 minutes.
5. Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on your knee and hip joints, preventing further wear and tear.
- Tip: Combine a balanced diet with regular low-impact exercise to achieve sustainable weight loss.
6. Supportive Devices
Using knee braces, orthotic insoles, or walking aids can help reduce joint strain and improve mobility.
Long-Term Prevention Tips
Preventing knee and hip pain requires a proactive approach to joint health.
1. Regular Exercise
Low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, or cycling can strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee and hip joints without overloading them.
- Recommended Exercises:
- Knee: Leg raises, wall sits, and gentle stretches.
- Hip: Perform hip bridges, side leg lifts, and yoga poses such as the cat-cow stretch.
2. Maintain Good Posture
Proper posture reduces unnecessary strain on your joints.
- How to Improve Posture:
- Sit with your back straight and feet flat on the floor.
- Avoid crossing your legs while sitting for long periods.
3. Wear Proper Footwear
Shoes with adequate cushioning and arch support can absorb shock and improve alignment, reducing strain on your knees and hips.
4. Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration supports joint lubrication and overall health.
When to See a Doctor
While home remedies can be effective, some situations require medical attention:
| When to Seek Medical Help |
|---|
| The persistent pain does not subside with rest or medication. |
| The joint may experience swelling, redness, or warmth. |
| The affected leg is unable to support weight. |
| Sudden, severe pain after an injury. |
FAQs About Knee and Hip Pain
1. What is the most common cause of knee and hip pain?
Osteoarthritis is the leading cause, but injuries, inflammation, and obesity are also common contributors.
2. Can knee and hip pain be prevented?
Yes, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and practicing proper posture can significantly reduce your risk.
3. Are there specific foods that help with joint pain?
Yes, anti-inflammatory foods like salmon, walnuts, spinach, and turmeric can promote joint health.
4. How long does it take for knee and hip pain to heal?
The recovery period varies depending on the cause. Mild pain from overuse may improve within days, while arthritis or significant injuries may require weeks to months of treatment.
5. Is surgery always necessary for knee and hip pain?
Surgery is usually considered a final option. Lifestyle changes, physical therapy, and medications can manage many cases.
6. What is the best painkiller for hip and knee pain?
Depending on the individual and the underlying cause of the pain, there is no universally effective painkiller for hip and knee pain. However, some common over-the-counter pain relievers that may be helpful include acetaminophen (Tylenol), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), and naproxen sodium (Aleve). Your doctor should help you choose a painkiller.
7. What is the best way to relieve knee pain?
There are a number of things you can do to relieve knee pain, including resting your knee, applying ice, taking over-the-counter pain medication, and wearing a knee brace.2 If your knee pain is severe or does not improve with home treatment, you should see a doctor.
8. What causes knee and hip pain at the same time?
There are many possible causes of knee and hip pain at the same time, including arthritis, injury, and repetitive stress. If you are experiencing knee and hip pain, it is important to see a doctor to determine the cause and get the appropriate treatment.
9. What causes pain between knee and hip?
There are many possible causes of pain between the knee and hip, including muscle strain, tendinitis, bursitis, and arthritis. If you are experiencing pain between your knee and hip, it is important to see a doctor to determine the cause of your pain and get the appropriate treatment.
10. What’s the best thing for hip and knee pain?
There are many things you can do to relieve hip and knee pain, including resting the affected joint, applying ice, taking over-the-counter pain medication, wearing a brace, and physical therapy.3 If your hip and knee pain is severe or does not improve with home treatment, you should see a doctor.
Conclusion
Debilitating knee and hip pain can be managed and prevented with the right approach. From understanding the causes and symptoms to incorporating effective remedies and prevention strategies, you can take control of your joint health.
If your pain persists or worsens despite trying these remedies, consult a healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation and treatment plan. Taking proactive steps now can save you from more significant joint issues later on and improve your overall quality of life.
Related Reads
- Top 7 Foods to Boost Your Brain Power
- 3 Warning Signs of Diabetes You Should Never Overlook
- Health Benefits of Air Potato (IKPALO)
Our Sources: thetlcpt.com And www.mountainvalleyortho.com
- Advertisement -


