Yeast infections, primarily caused by the Candida fungus, are common fungal infections that can affect various parts of the body. These infections can range from mild to severe, depending on the affected area and the individual’s overall health. While vaginal yeast infections are the most well-known, they can also occur in the mouth, skin, and internal organs in severe cases.
In this article, we’ll dive into the types of yeast infections, their causes, symptoms, preventive measures, and treatment options. Understanding these aspects can help you manage and prevent this common but potentially serious health issue.
What Are Yeast Infections?
Yeast infections occur when there is an overgrowth of the Candida fungus, which is naturally present in small amounts in the body. Factors such as a weakened immune system, hormonal changes, or antibiotic use can disrupt the balance of bacteria and fungi, leading to an infection.
Common Types of Yeast Infections
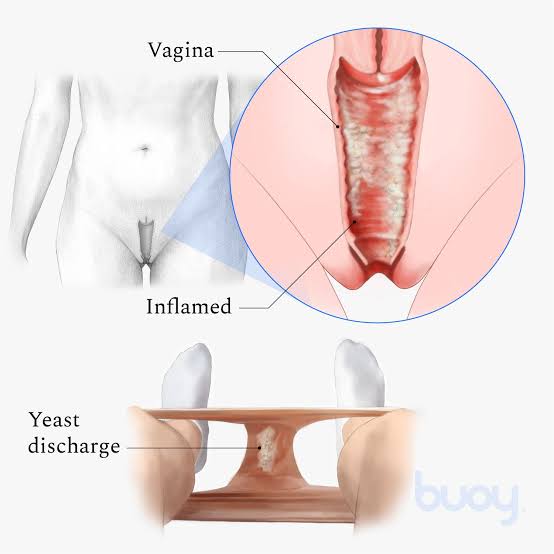
- Vaginal Yeast Infection (Vaginal Candidiasis)
- Affects the vagina and vulva.
- Symptoms include itching, burning, and a thick, white discharge.
- Oral Thrush
- Affects the mouth and throat.
- Symptoms include white patches, redness, and difficulty swallowing.
- Skin Yeast Infections
- It is prevalent in warm, damp regions such as the armpits, groin, and the spaces between toes.
- Symptoms include redness, itching, and a rash.
- Candidemia
- A bloodstream infection caused by Candida.
- Hospitalised patients or those with weakened immune systems often experience this.
- Invasive Candidiasis
- Candida causes a severe infection that can spread to internal organs like the heart, lungs, and brain.
- Symptoms include fever, chills, and organ failure.

Causes of Vaginal Infection
Factors that disrupt the natural balance of bacteria and fungi in the vagina often trigger vaginal yeast infections. Common causes include:
- Antibiotics: Kill beneficial bacteria, allowing Candida to overgrow.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, birth control pills, or hormone replacement therapy can alter vaginal pH.
- High Blood Sugar Levels: Individuals with diabetes are at higher risk.
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions such as HIV or chemotherapy lead to increased susceptibility.
- Poor Hygiene: Wearing tight, damp clothing or using scented products can promote fungal growth.
Invasive Candidiasis: A Serious Concern
While most yeast infections are mild and manageable, invasive candidiasis is a rare but life-threatening condition. It occurs when Candida enters the bloodstream and spreads to internal organs. This condition primarily affects individuals with weakened immune systems or those undergoing intensive medical treatments.
Risk Factors for Invasive Candidiasis
- Prolonged use of antibiotics disrupts the body’s natural flora.
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions such as HIV/AIDS, organ transplantation, or chemotherapy lead to increased susceptibility.
- Chronic Illnesses: Diabetes, kidney disease, and other chronic conditions can elevate risk.
- Hospital stays: Extended hospitalizations or mechanical ventilation can expose individuals to the infection.
- Surgical Procedures: Infections may occur after invasive surgeries.
Severe Yeast Infection Symptoms
Severe yeast infections, such as invasive candidiasis, can lead to serious complications. Symptoms include:
- The patient has a persistent fever and chills that are unresponsive to antibiotics.
- Organ failure is particularly prevalent in the kidneys, liver, or lungs.
- Respiratory Problems: Difficulty breathing or chest pain.
- Confusion or disorientation can occur when an infection enters the brain.
- Skin Lesions: Widespread rashes or sores.
If you experience these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
Treatment Options for Yeast Infections
The treatment for yeast infections depends on the type and severity of the infection.
Common Treatments
- Antifungal Medications
- Fluconazole: An oral antifungal commonly prescribed for yeast infections.
- Topical Antifungals: Creams or ointments for skin or vaginal infections.
- Amphotericin B is used for severe or systemic infections such as invasive candidiasis.
- Surgical Intervention
- In severe cases, surgical draining or removal of the infected tissue may be necessary.
- Intensive Care
- Patients with invasive candidiasis may require hospitalization and intensive care.
Home Remedies for Mild Infections
- Probiotics: Help restore the natural balance of bacteria and fungi in the body.
- Coconut Oil: Contains antifungal properties that can soothe mild infections.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: You can apply diluted ACV to the skin for topical infections or use it as a rinse for oral thrush.
How to Prevent Yeast Infections
Prevention is the best strategy when it comes to managing yeast infections. Here are some practical tips to reduce your risk:
- Maintain good hygiene.
- Keep skin dry, especially in areas prone to moisture.
- Change out of wet clothing, such as swimsuits or workout gear, promptly.
- Limit Antibiotic Use
- Only use antibiotics when prescribed, as they can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria.
- Manage Chronic Conditions
- Control underlying health issues like diabetes to reduce your risk.
- Boost Immune Health
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise regularly and get adequate sleep.
- Avoid Irritants
- Stay away from scented products, harsh soaps, and tight clothing that can irritate the skin.
- Practice Safe Sex
- Use protection to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections that may complicate yeast infections.
Is Candida a Sexually Transmitted Disease?
The fungus that causes yeast infections, Candida, is not considered a sexually transmitted disease (STD). However, sexual activity can occasionally trigger yeast infections for the following reasons:
- Transfer of Candida between partners.
- Irritation caused by intercourse.
- Lubricants or condoms can alter the pH of the vagina.
Practicing safe sex and maintaining good hygiene can reduce the risk of developing or spreading a yeast infection, even if it is not an STD.
FAQs About Yeast Infections
1. What causes yeast infections?
The Candida fungus overgrows and causes yeast infections. Factors like weakened immunity, antibiotics, hormonal changes, and chronic illnesses can contribute to their development.
2. Are yeast infections contagious?
Most yeast infections are not contagious. However, Candida can spread through close contact or shared items like towels, especially in individuals with weak immune systems.
3. Can yeast infections resolve on their own?
Mild infections may resolve without treatment, but it’s best to seek medical advice to prevent complications.
4. Are yeast infections common during pregnancy?
Yes, hormonal changes during pregnancy can increase the risk of vaginal yeast infections. Pregnant women should consult their doctor for safe treatment options.
5. How can I prevent recurring yeast infections?
Maintaining excellent hygiene, managing underlying conditions, and avoiding triggers like scented products can help prevent recurrence.
6. Can a man give a woman a yeast infection?
Yes, sexual activity can transfer Candida, even though yeast infections are not considered STDs. Maintaining good hygiene and practicing safe sex can mitigate the risk.
7. Can hot water reduce yeast infection?
Hot water alone won’t cure a yeast infection but can provide temporary relief from itching. Avoid using excessively hot water, which can irritate sensitive skin.
8. How do you flush a yeast infection out of your body?
Drinking plenty of water, consuming probiotics, and following a prescribed antifungal treatment can help flush out a yeast infection.
9. What cures yeast infections fast?
Antifungal medications like fluconazole or over-the-counter creams can provide immediate relief. For severe infections, consult a healthcare provider for appropriate treatment.
10. What are the main causes of a yeast infection?
The main causes include antibiotic use, hormonal changes, high blood sugar levels, and a weakened immune system. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk
The Role of Diet in Preventing Yeast Infections
A healthy diet plays a crucial role in preventing yeast infections. Incorporate the following foods into your meals to boost your immune system and reduce Candida overgrowth:
| Food | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Yoghurt | Contains probiotics that restore gut flora. |
| Garlic | Has natural antifungal properties. |
| Leafy Greens | Supports detoxification and immune health. |
| Coconut Oil | Contains caprylic acid, which fights Candida. |
| Cranberries | It inhibits fungal adhesion, especially in the urinary tract. |
Avoid refined sugars, processed foods, and alcohol, as these can promote Candida growth.
Understanding Asthma: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management
Long-Term Effects of Yeast Infections
While most yeast infections are treatable, untreated or severe cases can lead to complications, such as:
- Chronic Fatigue: Persistent tiredness due to systemic infections.
- Organ Damage: Severe cases such as invasive candidiasis can cause permanent damage to internal organs.
- Recurrent Infections: Immunocompromised individuals may experience recurring infections.
Final Thoughts
Yeast infections, though common, can range from mild to severe depending on the type and the individual’s overall health. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for managing these infections effectively.
For more severe infections like invasive candidiasis, early diagnosis and prompt medical intervention are critical to prevent life-threatening complications. By practicing proper hygiene, maintaining a balanced diet, and avoiding unnecessary antibiotics, you can reduce your risk of yeast infections.
Remember, if you experience recurring or severe symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for appropriate diagnosis and treatment. Your health is your top priority, and taking preventive measures can significantly enhance your well-being.
For more healthy tips and insights, stay connected and prioritize your health today!
Sources: Yeast Infection | Johns Hopkins Medicine , Cleveland Clinic Vaginal Yeast Infection: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment